France-An Introduction
Geography
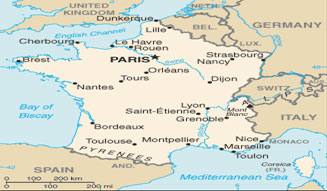 Area: 632,834 sq. km, of which 543,965 in metropolitan France and 88,969 in the overseas départements (DOM).
Area: 632,834 sq. km, of which 543,965 in metropolitan France and 88,969 in the overseas départements (DOM).
Rivers: Five major rivers flow entirely or partially in France: Loire, 1,012km; Rhine, French section, 150km (total 1,320); Garonne, 575km; Seine, 776km; Rhône, 812km.
Coastline: 7,000km.
Some popular sites: on the Channel, the cliffs at Étretat, Mont Saint-Michel (3.5 million visitors a year); on the Atlantic, Pointe du Raz (over 1 million) and Pilat dune; on the Mediterranean, the calanque fjords in Cassis and the bay of Saint-Tropez (Massif des Maures), the French Riviera, Nice, Cannes (Massif de l’Estérel).
Mountains: Two ancient massifs, Massif Central and Vosges, and three younger ranges, Alps, Jura and Pyrenees.
Climate: Temperate, oceanic and Mediterranean, prevailing westerly winds.
Population: 63.8 million on 1 January 2008. Second largest in the European Union after Germany (82.3 million) and ahead of the United Kingdom and Italy.
The Paris urban area, population 10 million, is the largest in the EU (ahead of London); equal second in France are Lyon and Marseille-Aix-en-Provence, population 1.35 million, and fourth, Lille, 1.1 million.
Administrative divisions
The traditionally centralised administration of France was radically modified by the decentralisation laws passed in 1982-1983.
Since then, central government has shared some of its responsibilities, particularly economic and cultural, with territorial communities.
France’s territorial communities are
Regions (22 in metropolitan France and 4 overseas). The largest are Midi-Pyrénées and Rhône-Alpes (over 40,000 sq. km). Most populated is Ile-de-France (11 million), well ahead of Rhône-Alpes;
départements (96 in metropolitan France and 4 overseas);
communes (36,778).
Political system
Bicameral parliamentary system: Senate (331 senators) and National Assembly (577 deputies).
The President of the Republic, elected for a five-year term, appoints the Prime Minister, who is the head of government. Nicolas Sarkozy, sixth President of the Fifth Republic, was elected on 6 May 2007. The voting age for all elections, local, national and European, is 18.
National anthem: the Marseillaise.
National holiday: 14 July, date of the capture of the royal prison, the Bastille, by revolutionaries in 1789. First celebrated in 1792.
The French Republic is a secular state. The principle of secularity (laïcité) is enshrined in the Constitution. It guarantees freedom of conscience and worship, equality of all before the law whatever their religion, and the freedom and neutrality of education.
France in the world
European Union: France was a founding member of the Common Market, the European Economic Community and the European Union. The country has continually worked to build European institutions, an integrated economic area and closer common positions on foreign policy. France will take over the Presidency of the European Union in the second half of 2008.
International cooperation: France is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council and other UN bodies. As such, the country participates in peacekeeping and human-rights operations around the world.
Development assistance: France supports the various UN programmes in this field: poverty reduction (UNDP), protection of children (Unicef), drug control (UNDCP). The country focuses on bilateral aid. Official development assistance in 2007 was €9.1 billion, 0.5% of GDP (2012 objective: 0.7%).
Humanitarian action: The Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs’ delegation for humanitarian action coordinates emergency relief abroad and maintains partnerships with relief NGOs.
Cultural exchanges: France has 144 cultural establishments abroad and a network of 283 Alliance Française centres. Campus France facilitates partnerships between French and international universities, recruits students from abroad and helps them during their stay in France. A local campus of the Sorbonne has been opened in Abu Dhabi.
The French language: More than 200 million people in the world speak French. French is one of the two UN working languages, the sole language of the Union Postale Universelle, and the main language of the African Union. Use of French throughout the world is supported by a network of over 440 schools at all levels in 135 countries. These are attended by a total of 250,000 French and local students.
Broadcasting: France’s international presence, already represented by the French-speaking channel TV5 Monde and RFI (Radio France Internationale), has been extended and enriched since December 2006 by France 24, an international news channel in French, Arabic and English, soon to be joined by Spanish, broadcast in 90 countries (Europe, Middle East, Africa).
Economy
GDP: France is the fifth largest economy in the world in terms of GDP – €1,792 billion in 2006. In Europe, it is third, behind Germany and the United Kingdom.
Growth is mainly based on the construction and public works sector and services. The 2007 data indicate a certain slowdown.
France is the largest agricultural producer in Europe. Income per farm worker has risen faster than in the traded sector as a whole.
Although the share of industry in the French economy is lower than in its three largest European neighbours, a number of major French groups are world leaders in their specialities: for example, Peugeot, Renault, Saint-Gobain, Michelin, L’Oréal, Air Liquide.
Productivity gains in the last fifteen years have been particularly marked in electrical and electronic consumer goods.
Major retail groups have seen intensive international growth. Carrefour has risen to second place in distribution, behind the US Wal-Mart. In construction and concessions, Vinci is the world leader.
Exports. France comes second here in Europe, with €386 billion in 2006 (behind Germany, its main partner) and second in the world (behind the United States) for agri-food exports, a staple of French foreign trade. But the country is beginning to lose market share to emerging countries.
France’s trade balance, however, continues to record a large deficit: -€29 billion.
FDI: With foreign direct investment of €58 billion in 2006, a constantly rising figure, France is the third country in the world in receipts of FDI, with all the consequent positive effects on employment.
Companies. The largest companies by market capitalisation in the CAC-40 index include Total and EDF, followed by banks and insurance companies (BNP-Paribas, Axa, Suez, Société Générale) and the steel group Arcelor-Mittal. France suffers from a lack of small and mid-sized firms, a sector that is strong in Germany and Italy in particular.
National debt: 63.9% of GDP in 2006.
Inflation: 2.8% in 2007 (euro zone average: 3.1%).
Population and living standards
Demographic indicators place France above the EU average.
Age structure: 24.7% under 20 and 21.3% over 60.
Life expectancy: 77.5 years for men (close to the European average), 84.4 years for women (2 years above the European average).
Fertility rate: 198 children per 100 women.
Retirement: Average retirement age: 58.8 years (EU-25 average: 60.9 years).
Income and employment indicators place France slightly above the European average.
GDP per capita: €28,356. Compared with an EU-27 base 100, France is at 112.8, the United Kingdom 118.1 and Germany 113.5.
Working hours per week (effective): 35.9 (Germany: 35.8; UK: 35.7).
Labour force participation: 63% (close to EU average; Denmark, 75.8%).
Unemployment rate: just over 8% in 2007 (EU-25: 8.7%).
Pre-tax minimum hourly wage: €8.44.
Minimum per month, 35-hour week: €1,280 on 1 July 2007.
Pre-tax average monthly salary: €2,440.
Income inequality: 3.45, ratio of top 10% household income to bottom 10% (EU-15: 3.42).
